Uranium and Norm/Tenorm
Radiological and Regulatory Assessment Services
Radiological and Regulatory Assessment of Legacy Uranium Projects and Sites
Providing technical support as the radiological Subject Matter Expert (SME) to the US Department of Energy’s Defense Related Uranium Mine (DRUM) program within DOE’s Office of Legacy Management. Program involves characterization, assessment, and prioritization of over 3000 abandoned (legacy) uranium mining sites that produced uranium ore for US defense programs prior to 1970. This work has involved (1) Development of radiological screening criteria based on projected radiological exposures to future public visitors of the sites under recreational and residential exposure scenarios; included analysis of multiple exposure pathways to assist prioritization for potential further action of these several thousand sites. These included several hundred sites on Tribal land requiring coordination with EPA Region 9 and integration of CERCLA with Atomic Energy Act requirements and (2) Support for the comprehensive radiological surrey program by performing field assessments and normalization studies for a number of radiological survey instruments being used to measure gamma exposure and dose rates at these DRUM sites. Through summer 2023, the radiological screening criteria and survey protocols Mr. Brown has developed have been used at over 2000 DRUM sites (See Health Physics June 2018, Volume 114, Number 6. pp. 588-601)
https://nucleus.iaea.org/sites/orpnet/resources/NORM%20X/Session%2021%20Steven%20Brown%20-%20.pdf
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Nuclear and Radiological Regulatory Commission (NRRC) – as Subject Matter Expert (SME) to NRRC in a staff augmentation role, provided support for the development of comprehensive regulations and guidance for uranium exploration, mining and milling and for preparation of associated license applications. Work involved review / comments to agency staff on draft regulations being prepared by anther contractor team which were then incorporated into the agency’s official comments back to the contractor. Work products also involved development of technical basis documents, similar to USNRC regulatory guides, for performance of environmental radiological monitoring and various operational health physics activities to assess worker dose at uranium mines and mills, including uranium extraction from phosphate production.
Provided an assessment for the client’s legal counsel on the adequacy of the previous remediation performed under the 1986 US Department of Interior Record of Decision relative to current standards of practice for public radiological protection and cleanup criteria as specially relevant to uranium mines and mills. This assessment included applicability of US EPA 40 CFR 190 and 192 and USNRC 10 CFR 40 Appendix A. Included the review and analysis of historical radiological survey data to ascertain adequacy and achievement of Data Quality Objectives and data usability.
For the former Midnite Uranium Mine Superfund Site on the Spokane Indian reservation in Washington, being assessed and remediated under EPA CERCLA requirements, developed a comprehensible Radiation Protection Program Plan and numerous health physics survey procedures for the monitoring, exposure assessment and exposure control of remediation (construction) workers. This project involves consolidation of approximately 18 M cubic yards of above-ground mine waste deposits and impacted soils/sediments into several existing pits. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) were prepared including specification of radiological instrumentation requirements for conduct of gamma surveys, for particulate and radon daughter air sampling, radon flux measurements, contamination control, external and internal dose assessment including bioassay, etc. Additionally, field procedures were developed, consistent with applicable MARSSIM requirements, to establish when cleanup criteria (radium 226 concentrations in soil) have been achieved using real-time field gamma surveys. Gained acceptance from the EPA on this radiological survey and verification approach, a result that is expected to save many millions of dollars in reduced sampling and analytical costs over the life span of the remedial action project.
Performed an analysis to determine if residual levels of radium 226 and natural uranium at this former uranium processing site had been reduced to levels that would meet Federal (United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission) and State of Texas (Texas Commission on Environmental Quality - TCEQ) requirements to permit release of this site for unrestricted use and to allow termination of its US Atomic Energy Act license. The analysis was based on the “Radium Benchmark Dose Approach” as defined by the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission (10 CFR 40, Appendix A; NUREG 1569 and 1620) using the Argonne National Laboratory RESRAD family of computer codes. The results indicated the residual radioactivity above background in soils meets the criteria of the benchmark dose approach as defined and applied by the USNRC, and therefore, the site could be released for unrestricted use under Federal (USNRC) requirements, even though some individual surface soil samples exceed the numerical criteria for uranium in soil established by TCEQ. The TCEQ and NRC concurred and the license was terminated.
Performed radiological assessments, surveys, and characterization of former (legacy) uranium processing and mining sites in New Mexico, Arizona, and Wyoming. These included the Quivira (NE Church Rock) site and Mariano Lake sites in New Mexico, the Sheep Mountain site in Wyoming, and legacy uranium sites in the Cameron District of Arizona. This work involved use of the RESRAD computer code and the USEPA PRG calculator to define radiological cleanup criteria in soil (e.g., pCi/gram Ra 226). Additionally, MARSSIM radiological survey methods were used as applicable.
Prior to 1985, performed radiological surveys and assessments at many “MED” (Manhattan Engineering District) sites which were similar to, or in some cases became FUSRAP sites (West Chicago, Apollo, Canonsburg, Weldon Springs, etc.). Similar to most of the FUSRAP sites, these were sites at which nuclear weapons program materials were processed and became contaminated with uranium, thorium, and/or radium and progeny. During the period 1998–2007, provided senior-level health physics and radiological risk assessment support and oversight at numerous FUSRAP projects including Maywood NJ, the St. Louis downtown and airport sites, Linde (Buffalo), Colonie (Albany), Ashland (Buffalo), Tonawanda (Buffalo), and others. Additionally, for many years, was a session organizer and co-chair for the FUSRAP technical sessions at the annual Waste Management Symposiums in Arizona.
Licensing and Operations of Uranium Recovery Projects
As Radiation Safety Officer for Westinghouse Uranium Operations (Wholly owned subsidiary of Westinghouse Uranium Operations was the Wyoming Mineral Corporation), developed and administered radiation protection, industrial safety, and environmental compliance programs for 5 commercial-scale licensed uranium recovery facilities and several smaller R&D plants, designed the radiation protection and associated environmental monitoring programs, and provided corporate E, S, H and license compliance oversight for in situ (leach) recovery facilities and uranium recovery facilities that extracted uranium as by-product from phosphoric acid production and copper mining. Line manager for industrial hygiene and safety, radiation protection and environmental compliance functions and corporate radiation safety officer under our NRC/Agreement state operating licenses. Supervised HQ and uranium plant staffs including over 40 hygienists, health physicists, industrial safety, and environmental professionals and technicians. Performed numerous license compliance and ALARA program audits at Westinghouse’s uranium fuel cycle facilities including uranium mines, mills, in situ recovery, and nuclear fuel processing facilities.
Participated in a study to compare radon monitoring and modeling techniques used to assess compliance to the 10 mrem / yr, public dose criteria of USEPA’s 40 CFR 61.22 emissions standard for radon-222 from underground uranium mines. The study involved comparison of effluent monitoring results from several operating underground uranium mines in the Four Corners area comparing EPA Method A-6 (continuous monitoring using flow-through scintillation cells) vs. Method A-7 (passive alpha track detectors). The study also included comparison of two EPA-approved dispersion and dosimetry codes, AERMOD and COMPLY-R, to assess potential differences in results obtained from these models. These included terrain effects and other environmental factors using local meteorological and demographic data from the mine site locations.
Supported the preparation of a number of USNRC and Agreement State license applications for uranium in situ recovery and several proposed conventional (including heap leach) uranium mills in Wyoming, Texas, Colorado, and New Mexico. Technical contributions included authorship of license application sections on radiation protection, accident analysis, public dose assessment, environmental monitoring, and for decommissioning plans. Designed and provided oversight of execution of preoperational radiological baseline programs involving sampling and analysis for radionuclides in soil, ground and surface water, air, and vegetation. This work was executed in accordance with US NRC Regulatory Guides 3.46, 3.8, 4.14, 4.15, 8.30, 8.31 and NUREGs 1569 and 1748. Used Argonne National Laboratory MILDOS computer code to assess public exposure during operations and RESRAD computer code to define future radiological remediation and license termination criteria in accordance with NRC’s “Radium Benchmark Dose Approach” as required by 10 CFR 40 Appendix A, Criteria 6(6). Several examples follow:
Prepared a hazard and risk assessment for the first new license application submitted for a conventional uranium mill in US in > 30 years; assisted in development of numerous program manuals and plans including radiation protection procedures manual, health and safety plan, emergency response plan, materials management plan, etc. Was the approved Radiation Safety Officer under the source material and milling license issued by the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment.
As lead licensing and radiological consultant on the Pena Ranch Project, assisted in defining the overall content and format for a USNRC license application (last conventional mill licensed in the US over 30 years ago). This work involved the integration of legacy USNRC licensing requirements for uranium mills per USNRC Regulatory Guides 3.5 and 3.8, with NUREG 1569 and 1748 requirements. Under Mr. Brown’s direction, compliance matrices were prepared to integrate the specific aspects of conventional uranium mills as described in RG 3.5 and 3.8, NUREG 1569 and 1748 with the applicable requirements for NEPA compliance in 10 CFR 51.45.
For what is probably the largest known uranium deposit in the US, Mr. Brown prepared a conceptual site model defining potential pathways of public exposure from radiological effluents expected from conventional uranium milling. These results could then be used to define sampling locations, media and radioanalytical requirements for preoperational baseline monitoring and environmental / public impact assessment during operations. Additionally, he was the lead author of a report entitled Assessment of Risk from Uranium Mining and Milling in Virginia, which provided both historical and current perspectives on the radiological risks associated with the potential development of Uranium recovery and processing operations (mining and milling) in Virginia at the Coles Hill Site.
Provided radiological support at various stages of the USNRC licensing application and review process for several uranium ISR licensees of the USNRC - Moore Ranch, Lost Creek, Nichols Ranch and ROSS ISR projects in Wyoming. During the license application preparation phase, authored radiological sections of the Environmental and Technical Reports on baseline radiological characteristics, radiation safety program, impacts of accidents, waste management, and quality assurance and performed dispersion and dose analysis using the MILDOS-AREA and RESRAD computer codes to assess potential dose to the public. Following license submission, work included assisting with responses to NRC Requests for Additional Information and providing other required radiological expertise to support the license application; assisted the owners in addressing pre-operational license conditions following receipt of their draft licenses.
Performed safety, health, environmental, and license compliance audits of two (Wyoming and Nebraska) uranium ISRs. These comprehensive audits involved review of procedures, training records, employee monitoring data, and related documentation to assess compliance with OSHA and USNRC requirements.
Supported the design and execution of preoperational radiological baseline programs for two ISR projects in Mongolia. Work involved the development of conceptual site models for assessment of environmental pathways of exposure to humans and other critical receptors; preparation of numerous field sampling and analysis procedures and health and safety plans. Plans and procedures prepared in accordance with international “best practices” (IAEA, Canada, U.S.)
Management of NORM in Other Industrial Applications
Acceptance of NORM (TENORM) at Industrial Landfills, Colorado - Two large, national industrial landfill operators requested the State of Colorado for permission to accept industrial wastes containing NORM and/or TENORM (uranium, radium e.g.) up to the limits allowable under Colorado regulations for industrial landfills (≤ 50 pCi / gram radium; ≤ 0.05 % natural uranium by weight). Mr. Brown assisted the operators in responding to a number of technical questions the State required to be addressed related to worker and public radiological risks that could be associated with acceptance of this material by the landfills. These projects included modeling of the radiological doses to workers and the public using the RESRAD and MILDOS computer codes (Argonne National Laboratory) and preparing Waste Acceptance Criteria (WAC) and associated procedures for acceptance and disposal of radiologically contaminated industrial waste streams. These assessments included developing dose estimates for a worker at the facility, located directly on top of the contaminated materials at the site and a nearby resident, potentially exposed to radon in air that is released from the landfill.
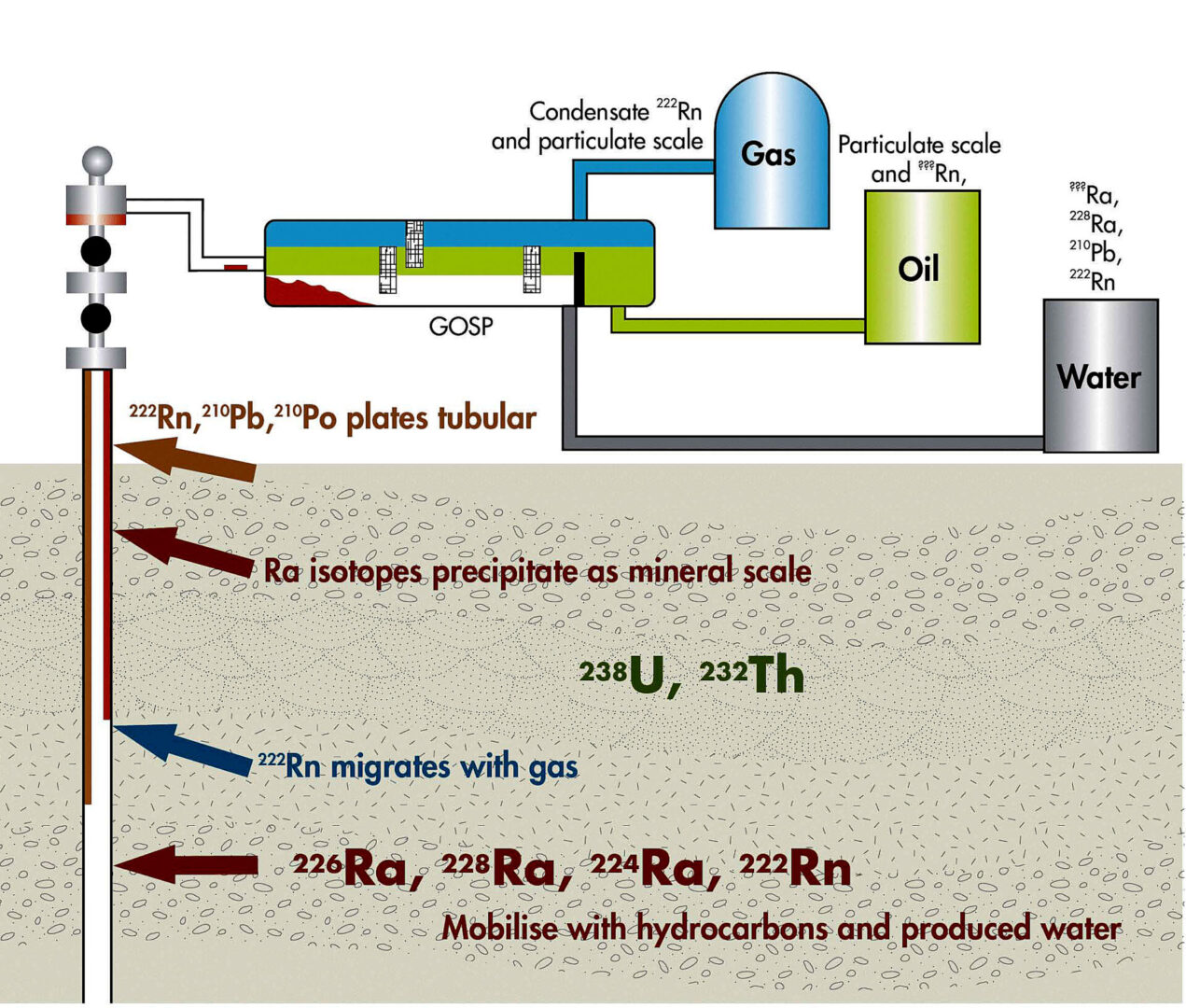
As radiological consultant to the Colorado Oil and Gas Association (COGA), have been providing assistance in a number of technical areas related to the development of TENORM regulations in Colorado. Have prepared COGA’s comments on the States’ TENORM studies and draft guidance, reviewed large radiological data basis to evaluate TENORM content of a number of O & G waste streams to assess potential candidacy as regulated material under the evolving regulations. Also have been evaluating various standard analytical methods being used for detection of TENORM nuclides (U, Th, Ra, Po, Pb) from perspective of accuracy, precision, and for minimizing analytical costs and turnaround times.
Since 2010, Mr. Brown has been assisting two Municipal Water Districts in Colorado on radiological matters related to their raw water treatment systems that provide all domestic water to hundreds of homes. The Ion Exchange (IX) media (water treatment residuals) which is used to remove the NORM radionuclides (uranium and radium) from their natural wells was determined to be “licensed material“ under State of Colorado regulations requiring a radioactive material license. Since preparing the initial license applications and subsequent issuance, Mr. Brown has served as the Radiation Safety Officer (RSO) under these licenses. His responsibilities as the RSO have included providing initial and annual refresher radiation safety training to plant operators, design and oversight of radiological surveys, worker dosimetry and public / environmental monitoring programs, and preparing and maintaining license-related SOPs.
Designed and executed radiological surveys to assess potential for worker radiation exposure from NORM / TENORM materials for two large Denver area municipal water districts serving hundreds of thousands of users. These projects involved conduct of radiological surveys in seven water treatment plants to determine real-time gamma exposure rates and use of longer-term radon (track – etch) and gamma dosimeters (OSLs) placed throughout the facilities for approximately 30-day periods. This comprehensive radiological monitoring program demonstrated that the radiation exposure to workers appeared to be consistent with natural background radiation exposure in Colorado.
Completed a worker dose assessment for a solid waste processing facility in Colorado that receives a variety of wastes from oil and gas exploration and production activities. Because of the potential for TENORM wastes being received, the State regulator requested the operator to conduct a human health risk assessment (dose assessment) for the facility. The assessment was based on the assumption that 50 picocuries per gram of naturally occurring radium 226 (Ra-226) would be present in all solid waste materials processed and temporarily stored within these facilities. The potential for both external radiation exposure (via exposure to gamma rays) and internal exposure (via inhalation of dusts and radon gas) were both evaluated in this assessment.
Since 2019, has been the Radiation Safety Officer for a water treatment plant in Winter Park, Colorado. This plant treats natural waters that drain from the Moffat (Railroad) Tunnel. The water must be treated prior to release to the Frazer River. As a result of the treatment process, a waste cake sludge is produced that contains greater than 1000 ppm natural uranium and is, therefore, licensed source material under the US Atomic Energy Act. The plant is licensed by the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment.